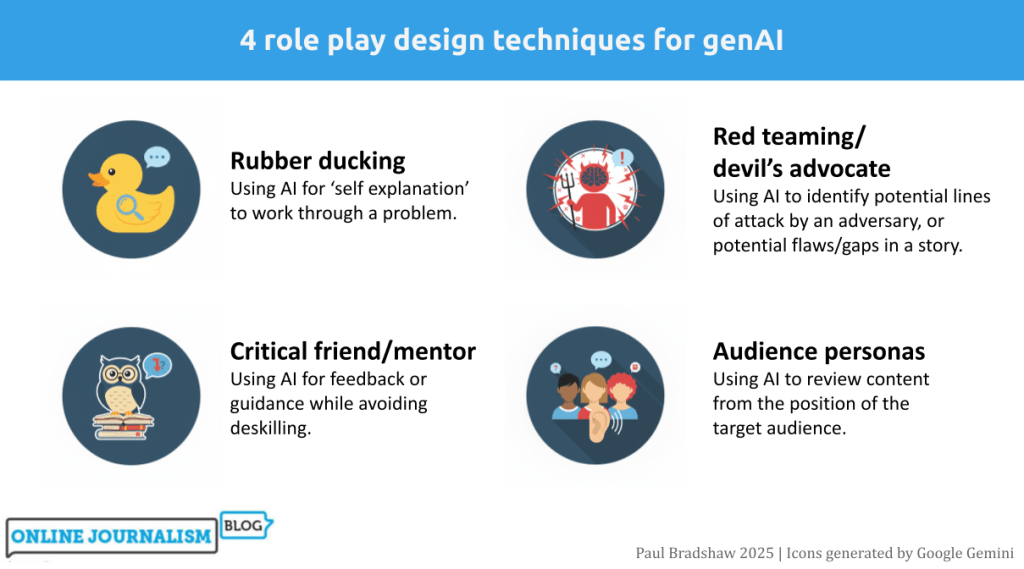
One of the most productive ways of using generative AI tools is role playing: asking Copilot or ChatGPT etc. to adopt a persona in order to work through a scenario or problem. In this post I work through four of the most useful role playing techniques for journalists: “rubber ducking”, mentoring, “red teaming” and audience personas, and identify key techniques for each.
Role playing sits in a particularly good position when it comes to AI’s strengths and weaknesses. It plays to the strengths of AI around counter-balancing human cognitive biases and ‘holding up a mirror’ to workflows and content — and scores low on most measures of risk in using AI, being neither audience-facing nor requiring high accuracy.
Continue reading
